Gilgit baltistan located in the extreme north of Pakistan is a land of breathtaking mountain glaciers rivers known as water tower of Pakistan . It holds some of the largest glaciers outside the polar region. These glaciers feeds the Indus river making the region essential for national water and energy security.
However despite this vast hydro-power potential many communities in GB still face limited access to electricity .Reliable energy is crucial for livelihoods ,education, healthcare and climate resilience in this remote mountain region where harsh winter and difficult terrain make life dependent on energy access.
Table of Contents
ToggleChallenges for Green Energy in Gilgit Baltistan
Current Energy Situation
At present majority of Gilgit Balistan’s energy come from diesel generator of small hydro power plants which are often insufficient for local demand .Frequent power outages and low voltage are common ,especially in winter when river flow decrease and hydro generation drops.Only about 14% of household are connected to the national grid,and imported diesel fuel is expensive due to transportation difficulties through mountain passes.This dependence on costly and polluting energy sources limits economic growth and adds to carbon emission.
Climate related risks
Climate change poses a challenge for the region’s energy future.Melting glacier and glacial lake outburst floods threaten not only communities also energy infrastructure such as micro hydro plants and energy transmission lines.Landslide triggered by heavy rainfall earthquake often damage roads and power systems isolating villages for weeks.
Rising temperature are accelerating glacier retreat which could initially increase river flow but eventually lead to reduced water availability, making hydro-power generation less predictable in the long run.
Caption:
📷 Seasonal low-flow in a Himalayan stream impacting hydropower potential (Source: Dawn, 2025).
Socio Economic Barriers
Many Households in GB have less income level, which limit their ability to invest in solar panels or energy efficient technologies. Technical expertise in renewable energy installation and maintenance is also scarce.
In several areas ,energy decisions are influenced by gender based social roles where women though most effected by energy shortages-are rarely included in planning. Additionally the fragemented ownership of water rights among villages leads to dispute among over the use of local streams of hydro projects, slowing implementations.
Policy landscape
Pakistan’s National Renewable Energy Policy (2019) and Energy Conservation Act (2016) provide frameworks for promoting renewable. However at the provincial level, Gilgit Baltistan lacks the strong institutional capacity and financial support needed for large scale implementation.
Policies exist paper but are rarely translated in local actions. There is no directed incentives or provincial regulations for renewable energy investment which discourages private companies from entering the market.
Enviromental Safeguard
Large Dams are not suitable for GB fragile mountain ecosystem. Poorly planned hydro-power plants can disturb aquatic habitats, while unassesed wind projects may impact bird migration routes. Moreover ,many areas face GLOF risks, so careful environmental impact assessment are essential before project approval. Balancing clean energy development with ecological protection remains a continuous challenge.
Opportunities for Green Energy in Gilgit Baltistan
Renewable Resource Map
Despite these challenges in Gilgit Baltistan holds exceptional renewable energy potential.
Solar energy: High altitude and long daylight hours make GB promising for solar PV. Studies show irradiance level above ~4 kWh/m²/day in many areas of GB.
Hydropower: Official data from Water and Power Department of Gilgit Baltistan show a currently installed capacity of around 185.6MW(hydro + thermal total ≈ 211 MW).
Wind Energy: While detailed wind mapping is still limited.GB terrain and valley’s are are favorable for wind installation with recorded speeds around 6m/s or higher in some zones.
Caption: Monthly average solar radiation in Gilgit and Skardu city (Source: ResearchGate, 2023)
Success Story -Community Micro-Hydro
Community -run -hydro-power-projects have shown impressive local benefits Over 169 micro- and mini-hydro plants, with a combined capacity of ~18.6 MW currently serve about 250,000 people in rural GB. These community owned systems improved livelihoods, support local enterprises and reduced diesel dependence-demonstrating that decentralized clean power is practical in mountain settings.
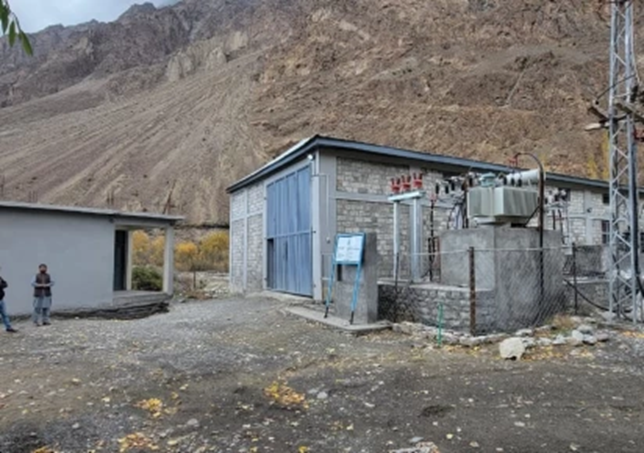

Caption:
📷 Community-managed micro-hydro plant in a Himalayan village supplying electricity to remote homes and schools (Source: Scroll.in, 2023).
Solar Mini Grids
Solar energy adoption is rising quickly. The federal Government recently approved a 100MW solar PV project for Gilgit Baltistan through ECNEC in 2025.
In Parallel ,smaller rooftop PV systems for schools, health centre and markets are expanding ,providing off grid reliability with battery storage .These mini hybrid grids are increasingly and suited to remote valleys where grid access is limited.
Caption: A solar mini-grid installation in Gilgit-Baltistan providing power to remote communities (Source: Cipher News, 2024).
Hybrid Wind Hydro Battery System
Hybrid system combining small hydro,solar or wind energy with batteries can stabilize electricity supply across seasons.Although detailed GB specific cost studies are limited,research from similar mountanious regions show that these system significantly lower life cycle and improve reliability compared to diesel generation.
Financing Mechanisms
Scaling renewable energy in GB requires stable funding. Green energy financing can come from Green Climate Fund, Asian Development Fund climate programs, public private organizations and community revolving funds. The recently sanctioned 100 MW solar project illustrates how federal and donor-level finance can accelerate energy access.
Social Acceptance and Cultural Values
Respecting community traditions and scared natural sites is vital for success.Projects that involve residents in decision making and offer fair benefits sharing have shown high trust and sustainability .Inclusive Planning also reduces the likelihood of conflicts over resource use.
Market Oppurtunities
Renewable create new business prospect in growing GB’s tourism sector. Eco-lodges, trekking camps, and guesthouses powered by solar or micro-hydro demonstrate GB potential for sustainable mountain tourism. In future, mini-grid linkages could allow power exports to adjacent valleys.
Digital tools and Data
Digital mapping and remote sensing enhance renewable energy planning.GIS based tools now assist in identifying optimal sites for hydro and solar plants while real time dashboard track generation,storage,and weather condition improving transparency and performance monitoring.
Future Scenarios (2030)
If GB continues its current trajectory many areas will remain energy poor.However a renewable led pathway could lift electricity access above 80% by 2030 boost local employment and cut emissions sharply.Realizing this scenario depends on investment and climate resilient planning.
Call for Actions for Companies
Private firms can contribute by financing micro hydro plants, installing solar grids or supporting local skill programs. Corporate social responsibility partnership that focus on energy access and inclusion can strengthen both business visibility and community development.
Conclusion
Gilgit Baltistan stands at turning point between persistent energy ,poverty,and a sustaianable energy future.Despite it challenges of geography and limited infrastructure ,the regions abundant water,sunlight,and resilient communities offer the foundation of green energy revolution .With informed policies ,inclusive governance and steady investment ,GB can lead Pakistan’s renewable energy transformation lighting the mountains sustainably for generations to come.