Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Land Use Mapping?
The process of determining and classifying the many uses of a given piece of land is known as land use mapping. Residential, commercial, transportation, and agricultural development are some examples of these activities.
Topographic maps, land allocation plans, aerial photographs and statistical data are typically used to construct land use maps. These maps can be used to track trends in development, spot patterns in urban land use, and spot any problems brought on by wasteful land use. An area’s natural resource degradation, for instance, could be depicted on a land use map.
High-resolution maps are crucial for decision-makers in a range of government agencies and economic sectors, as land use is changing quickly. Important subjects like planning and land conservation are better understood thanks to land use maps. Maps are used by national governments to spot patterns, establish priorities for land planning, and allocate funds. Additionally, they are becoming more and more helpful in planning for future growth.
The role of GIS in land mapping
A Geographic Information System (GIS) is an effective tool for mapping land usage in detail, allowing for highly accurate data collecting, visualization, and analysis. Professionals like environmental managers, urban planners, and disaster response teams can better understand how a certain region of land is being used with the aid of GIS.
GIS enables users to do more thorough analysis and produce intricate visualizations that show linkages, patterns, and changes in land use across time. In terms of development, conservation, or catastrophe preparedness, this enables decision-makers to make more strategic, sustainable, and informed decisions.
The capacity of GIS technology to convert complicated datasets into visually understandable maps is one of its main benefits. In order to facilitate navigation and interpretation of intricate spatial interactions, these maps frequently incorporate interactive 2D and 3D representations. In the end, GIS improves the capacity to effectively plan and manage land use, guaranteeing improved results for environmental and human systems.
Understanding Basics of Land Use Mapping in GIS
Land use mapping using GIS technologies allows for detailed analysis of urban growth, zoning patterns, and land resource management.In GIS, land use mapping entails gathering and arranging comprehensive data regarding the many uses of the land. Aerial photography, field surveys, satellite imaging, and existing land records are some of the common sources of data used in land use mapping. Every source adds significant information that completes the image of the land and how it is used.
GIS tools play a central role in managing and analyzing this data. They help users:
Digitize land parcels:
This entails transforming survey data or paper maps into digital representations that are simple to store, modify, and examine in a GIS system.
Assign attributes:
Specific characteristics, such as ownership details, zoning classifications, land use type, or legal constraints, are assigned to each parcel of property.
Conduct spatial analysis:
GIS enables the analysis of the interactions between various land uses, including the proximity of farms to water sources, the impact of urbanization on forests, and the locations of potential new roadways without causing environmental damage.
Generate thematic maps:
These are specialized maps that visually emphasize particular kinds of information; for instance, they might exclusively display residential regions in one color and agricultural lands in another. Complex data is considerably simpler to comprehend and convey as a result.
Land use mapping with GIS ensures accuracy (since digital tools minimize human error), consistency (since updates and classifications follow preset criteria), and ease of updating (since digital layers can be easily updated when changes occur, such as new construction or land re-zoning).
Applications of GIS in Land Use Mapping
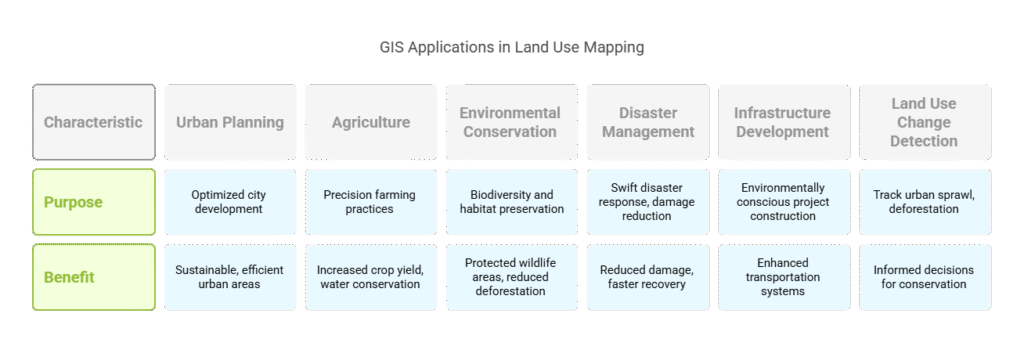
There are numerous significant uses for GIS (Geographic Information Systems) in mapping land use in various domains. Here is a brief description of its usage and context:
Urban Planning
Better city planning is made possible with GIS. It enables them to choose the ideal sites for homes, parks, educational institutions, and medical facilities. Planners can plan infrastructure, such as roads and water systems, and separate areas into residential, commercial, and industrial zones by examining detailed maps. Cities become more sustainable, efficient, and well-organized as a result, particularly in regions with sizable and expanding populations.
Agriculture
Farmers and academics utilize GIS in agriculture to control water consumption, monitor crop health, and engage in precision farming. GIS data, for instance, can be used by farmers to identify areas that require additional irrigation and to prevent overwatering of already healthy areas. This promotes more sustainable farming methods by increasing crop yield and conserving water.
Environmental Conservation
When it comes to environmental protection, GIS is quite helpful. It aids environmentalists in tracking protected wildlife areas, mapping forests, and tracking deforestation. Conservation teams can help preserve biodiversity by utilizing GIS to identify the locations of endangered species and take action to safeguard their habitats.
Disaster Management and Mitigation
When it comes to anticipating and responding to natural disasters such as earthquakes, landslides, and floods, GIS is essential. It enables emergency crews to respond swiftly and reduce damage while also assisting in the identification of risk locations. In order to facilitate quicker recovery operations following disasters, GIS also aids in determining the level of damage to homes, infrastructure, and land.
Infrastructure Development
GIS makes it considerably simpler to build big projects like utility lines, highways, and railroads. These networks can be created by planners with the least amount of environmental damage. Additionally, GIS is utilized to enhance transportation systems, lowering fuel use, traffic jams, and trip expenses.
Land Use Change Detection
Tracking changes in land use over time, such as urban sprawl or deforestation, is made possible using GIS. GIS offers comprehensive data that aids governments and environmentalists in making better decisions to preserve the environment and properly manage urban growth through the use of satellite imagery and time-lapse analysis.
GIS is a potent tool that aids in the effective management of land use in a variety of contexts, from farming and urban development to disaster relief and environmental preservation. Smarter, more sustainable decision-making is supported by GIS, which provides comprehensive, real-time spatial data.
Looking for Professional Approach and Quality Services?
Contact usTools and Techniques for Land Use Mapping in GIS
A number of crucial instruments and methods are employed in GIS-based land use mapping in order to efficiently gather, process, and update land data:
Remote Sensing:
Using satellite imagery to view the Earth’s surface is known as remote sensing. It assists in identifying the different forms of land cover (forests, rivers, and cities) and tracking alterations over time. This is essential for producing land use maps that are up to date without requiring frequent fieldwork.
Image Classification:
Using satellite photos, this method automatically classifies various forms of land cover. Users direct the system by identifying sample areas in supervised categorization. In unsupervised classification, the system uses data patterns to automatically categorize different types of land. Both approaches increase accuracy and expedite the mapping process.
Ground Truthing:
Field crews physically visit sites to confirm the satellite or aerial picture data in order to guarantee the accuracy of the maps. This procedure, known as “ground truthing,” helps land use maps become more reliable by fixing mistakes.
Geospatial Modeling:
Based on existing trends, geospatial modeling makes predictions about future changes in land use through simulations. It can simulate, for instance, how a city can grow over the next ten years or how farmland might decrease if urbanization persists.
Digitization:
Digitization is frequently used to transform older, paper-based maps into digital GIS layers. This procedure makes it possible to incorporate priceless historical data into contemporary GIS systems, which facilitates management and updating.
Change Detection Analysis:
This method uses several photos taken at various points in time to track and examine changes in land usage over time. It is crucial for monitoring changes in agricultural patterns, urbanization, and deforestation.
Benefits of Land Use Mapping
For communities and governments alike, land use mapping offers numerous significant advantages, particularly when carried out using GIS:
Better Planning and Decision-Making:
Maps of land usage provide a clear image of land use. This ensures balanced development by assisting planners and authorities in more prudently and effectively allocating resources, such as roads, schools, and hospitals.
Environmental Protection:
Land use mapping aids in environmental protection by locating sensitive regions such as wetlands, forests, and wildlife habitats. This guarantees that natural resources are protected for upcoming generations and aids conservation efforts.
Economic Growth:
The ideal sites for farms, housing projects, and industries are determined by careful land use planning. This encourages investment, generates employment, and boosts economic expansion in general.
Disaster Risk Reduction:
Authorities can take preventive action by mapping areas that are vulnerable to landslides or floods. It lowers the possibility of property and human harm and makes improved catastrophe preparedness possible.
Transparency:
Public access to land use maps frequently enables communities to observe how land is being used or developed for the future. This transparency promotes public involvement in decision-making processes and fosters confidence.
Best GIS Software for Land Use Mapping
Land use mapping is done using a number of well-known GIS software programs:
AI Geo Navigator
Ai geo Navigator is the Best GIS Mapping & GIS Consulting Services Company in Pakistan.AI Geo Navigator is a next-generation GIS solution that integrates artificial intelligence with geospatial data for smarter land use mapping and analysis. It uses machine learning to automatically identify land use patterns, classify land types, and optimize spatial analysis.
ArcGIS:
A strong instrument that many organizations use. For the creation, analysis, and visualization of land use data, it provides comprehensive tools. It provides sophisticated spatial analysis and is quite customizable.

QGIS:
An open-source, free substitute for ArcGIS. Because it supports numerous plugins that enable in-depth mapping, analysis, and customization, it is frequently utilized. For professionals and researchers on a tight budget, it’s a good choice.

Google Earth Engine:
A cloud-based tool that provides access to large datasets from satellites. It facilitates the rapid analysis of vast volumes of data and the simple and effective creation of land use maps.