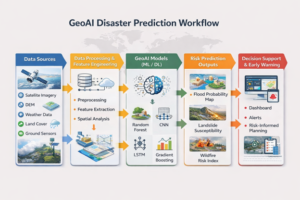
In a world increasingly driven by data, knowing where things happen is just as important as knowing what is happening. Whether it’s planning smarter cities, responding to natural disasters, tracking environmental changes, or improving public health infrastructure, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play a critical role.
As the heart of this spatial revolution are GIS Specialists professionals, who turn raw geographic data into actionable insights. But what does a GIS Specialist do? How do they collect and manage data, and how is their work shaping decision-making across industries?
This blog explores the role, skills, tools, and career path of a GIS Specialist, highlighting how their expertise is essential in solving real-world challenges across diverse sectors.
Table of Contents
ToggleWho is a GIS Specialist?
A GIS (Geographic Information Systems) Specialist is a specialist who applies geographic data to map and analyze data to make informed decisions on. They have a significant importance in different fields inclusive of urban and rural development, environmental science, transport, calamities, agriculture, and health care services.
A GIS specialist is mainly tasked with the duty of acquiring, sorting, storing, analyzing, and disseminating geographic information. This entails data collection done from other sources such as maps from space, the Geographic Information Systems, ground surveys and from the database. Once the data has been collected, purification is done, and the data is inputted into the GIS software so that it can fit the need of a particular goal.
Geographic information scientists perform geospatial analysis to model given conditions, identify characteristics in space and/or temporal dimensions and factors that may affect location. In particular, they can define regions vulnerable to flooding, define regions suitable for creation of new objects, or consider the areas of deforestation. Such information is provided in a way of maps, graphs and reports so as to facilitate in planning.
Some of these tools are GIS software such as ArcGIS and QGIS, and programming skills may be applied using programming languages like Python, SQL, or R for automation and analysis. It also entails preparing data graphics and maps that will best represent different spatial findings in a manner that is functional.
Beside technical competencies, the GIS Specialist should solve problems and be able to work in a team. Sometimes they work with city prognosis, engineers, environmental scientists, and other government officers to make sure the projects incorporate sound and meaningful geographical information.
In general, a GIS Specialist is the connection between the data gathered and their practical application in some organization. It has been providing their support to improve development, better utilization of resources, and good policymaking for both the governmental and non-governmental organizations.
What does a gis specialist do?
A GIS (Geographic Information Systems) Specialist helps to gather, process and present geospatial data to assist with the decision making process and find solutions to various issues. They input data into specialized GIS software such as ArcGIS or QGIS to handle datasets, analyze data geographically and create maps that map information relating to the data.
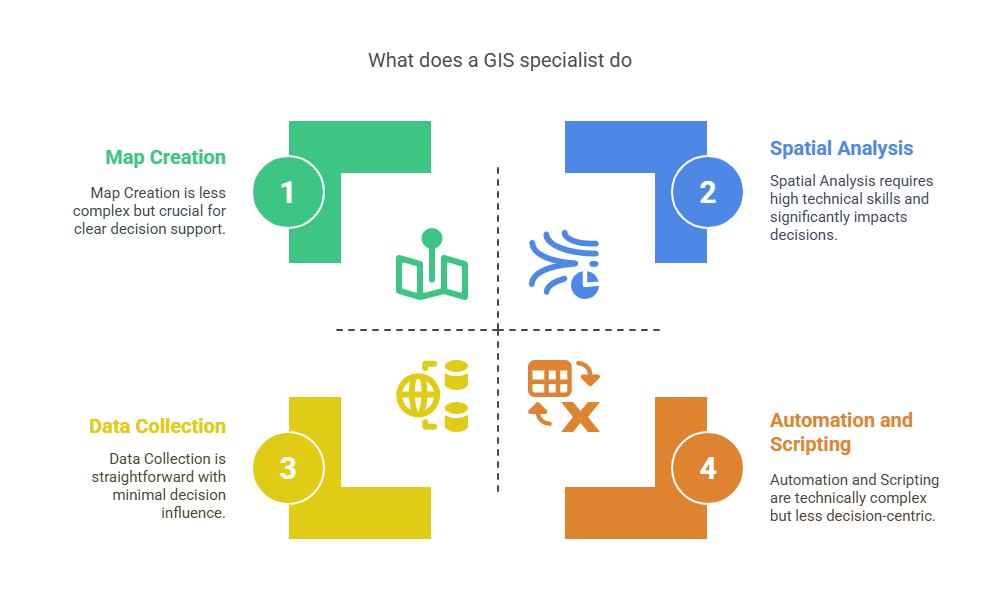
Key tasks include:
- Data Collection: Collecting data from diurnal GPS, satellite imagery, fi eld surveys, or other relevant databases.
- Data Management: GIS database: storing and organizing spatial data.
- Spatial Analysis: Performing operations like proximity, overlay, and network in order to find valuable information.
- Map Creation: Defining the ways of presenting maps and other visual aids to support the delivery of the results clearly.
- Problem-Solving: Underpinning urban and environmental planning, systems for disease and virus control and other industries which require geographical intelligence.
- Automation and Scripting: Applying simple scripting languages such as Python and SQL to support and improve the flow of documents and data.
The GIS specialists find their application in a wide range of industries such as government, consulting firms, transportation, utility companies and the organizations involved in management of emergencies. Such tasks include planning infrastructure, computing changes in the climate, logistics in choosing the best routes, management of resources in the natural resources sector, and disaster management.How to become a gis specialist
How to become a gis specialist
Therefore, to get the position of a GIS specialist, one needs to first complete a bachelor’s degree program in GIS and RS. They include general geographical knowledge, the ability to think geographically and the knowledge of how to handle geographical data.
Undergraduate level it is helpful mainly to take classes that are focused on GIS, remote sensing, cartography and spatial analysis classes. Further, some employees may also seek a certificate program in GIS or a master’s degree in geoinformatics or geospatial technologies to gain more advanced knowledge and get a competitive edge in the job market.
Internships, research projects or entry level positions as a GIS technician are useful to gain relevant work experience in this line. The requirements are familiarization with GIS applications like Esri’s ArcGIS, QGIS, or tools like Google Earth Engine or ERDAS Imagine.
However, prior experience in coding with programming languages such as Python, R or SQL for automating some tasks and executing geographical analysis becomes vital. Specialization in the use of satabases and systems, examples of these include spatial databases, web mapping platforms, and GPS equipment are also an added advantage.
The role of GIS Specialist also demands analytical thinking, problem solving and mastery of communication since most of the time they report their findings to a group of people from different fields. The use of professional certifications like Esri Technical Certification or GISP (Certified GIS Professional) will help in solidifying your credibility when working with clients and employers.
Last of all, the increased growth in the geospatial technologies, going to conferences and participating in the gis community is another important factor that will help in the progressive development of the field of gis. Education combined with the skills in technology and gaining experience on the field, one is prepared for a career of a GIS Specialist in areas such as environmental and urban planning, transference, health, and other emergency services.
Have Questions or Need GIS Expertise?
Get in Touch!GIS Specialist Job Responsibilities
A GIS (Geographic Information Systems) Specialist is responsible for collecting, processing, and mapping geographical information to aid in decision making process in different fields including land development, environmental conservation, transportation, and emergency services.
They perform geospatial analysis with a focus on software to analyze and understand large spatial and geographic data to create maps and present them to clients. Below are some of the common duties of a GIS Specialist:
Data Collection & Acquisition
- Gather geographic and spatial information by applying GPS, surveying the field, satellite imagery and remote sensing.
- The obtained external data have to be analyzed for their further compatibility and reliability coming from a third-party source.
Data Management
- Drawing, developing, and updating the spatial databases and GIS layers.
- To achieve this, businesses should be able to synchronize and make data accurate in all aspects of the organization.
- Check and filter the given data and write the metadata.
Spatial Analysis & Geoprocessing
- Apply geographical techniques to find the regional patterns and relationships.
- It is required to perform one or more types of analysis namely buffer, overlay, interpolation, as well as suitability analysis.
- Models to represent spatial scenarios in order to use the end results for planning and forecasting purposes.
Cartography & Visualization
- Ensure the production of professional high-quality static and interactive maps.
- Submit feature services, maps and apps to ArcGIS Online, use other apps and create 3D models.
- Ensure that the maps created follow the principles of cartography to facilitate proper communication and simplify the message being passed across.
Software & Tools Utilization
- This includes using GIS applications like ArcVIEW, ArcGIS, QGIS, ENVI and MapInfo along with the remotely sensed lineaments.
- Other scripting languages that can be utilized include; Python, R or SQL for scripting and automation.
- Deal with the Geographic Information System (GIS) and software’s like PostGIS and Oracle Spatial and with the help of Applications Programming Interface (API).
Interdepartmental Collaboration
- This means working with engineers, planners, environmental scientists, and IT experts effectively.
- Create clear and comprehensible reports and summaries with consideration to be able to convey technical information to different stakeholders effectively especially to the decision makers.
- Deliver user support; training of GIS tools and systems.
Project Development & Support
- Requirements For the Position Shall include: assist in planning and executing GIS related projects.
- Describe how the spatial analysis tasks will be conducted, the time that it is expected to take and what it is expected to produce.
- It is especially important to document all the foregoing workflows and project reports for future reference purposes.
System Maintenance & Integration
- Identify, diagnose and provide possible solution on any technical problems emanating from GIS systems.
- Fully embed GIS with other enterprise systems like ERP, CRM and asset management systems.
Compliance & Continuous Improvement
- Comply with the set data governance standards and regulatory frameworks.
- While it is necessary for the novice professional to keep abreast with the latest advancement in the business and technologies in the industry of Geospatial Technology.
- As part of the recommendation, the following professional development activities are recommended by this paper: Attending of workshop/seminars, Attending of conferences.
Key Skills for GIS Specialists to Advance Their Careers
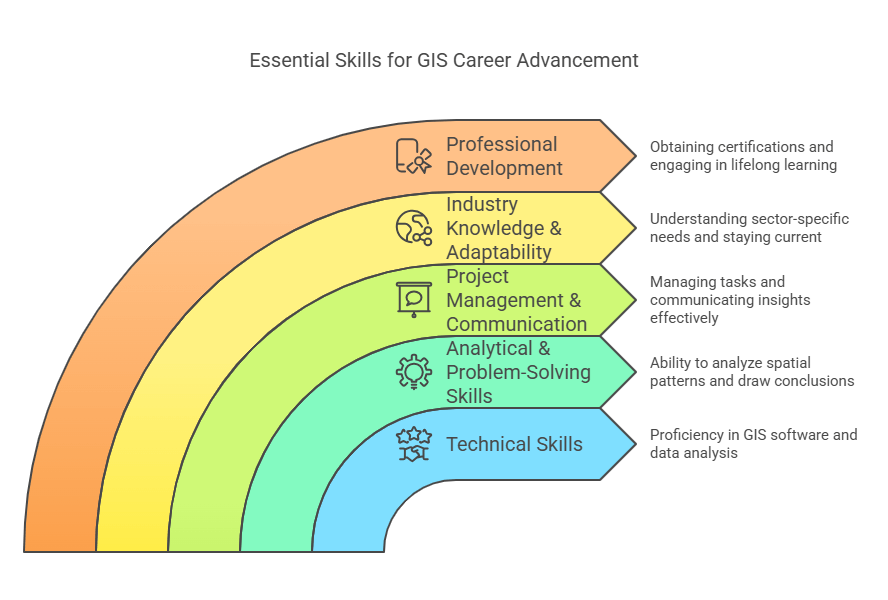
Technical Skills
- GIS Software Proficiency: Expertise in tools like ArcGIS, QGIS, MapInfo, and ERDAS Imagine.
- Remote Sensing: Ability to analyze satellite imagery and aerial photography.
- Spatial Analysis: Strong command of geoprocessing, network analysis, and raster/vector operations.
- Programming & Automation: Skills in Python, R, or JavaScript for scripting and building GIS applications.
- Database Management: Experience with spatial databases like PostGIS, SQL Server, and Oracle Spatial.
- Web Mapping & Development: Familiarity with platforms like ArcGIS Online, Leaflet, and Mapbox for interactive maps.
- Data Visualization: Ability to design clear, user-friendly maps and dashboards.
Analytical & Problem-Solving Skills
- Critical Thinking: Ability to analyze spatial patterns and draw meaningful conclusions.
- Attention to Detail: Ensuring data accuracy and consistency during analysis and visualization.
- Modeling & Forecasting: Applying spatial models to simulate scenarios and predict outcomes.
Project Management & Communication
- Project Planning: Managing GIS tasks, timelines, and deliverables effectively.
- Documentation: Maintaining detailed records of workflows, methodologies, and metadata.
- Stakeholder Communication: Translating complex spatial data into actionable insights for non-technical audiences.
- Collaboration: Working closely with planners, engineers, scientists, and decision-makers.
Industry Knowledge & Adaptability
- Domain Expertise: Understanding sector-specific needs (e.g., urban planning, agriculture, disaster management).
- Regulatory Awareness: Familiarity with data governance, privacy, and open data policies.
- Adaptability: Staying current with evolving GIS technologies and methodologies.
Professional Development
- Certifications: Obtaining credentials like GISP (Certified GIS Professional) or Esri Technical Certifications.
- Lifelong Learning: Attending workshops, conferences, and engaging in online GIS communities.
Conclusion
The role of a GIS Specialist is much more than working with maps—they are problem solvers, analysts, and storytellers who use spatial data to guide important decisions across a wide range of industries. From managing environmental resources to improving public safety and urban infrastructure, their work ensures that geographic data is not only collected but transformed into meaningful insights.
With growing demand for spatial intelligence in both the public and private sectors, GIS Specialists are becoming increasingly vital to data-driven decision-making in the modern world. Whether you’re considering this as a career or collaborating with one on a project, understanding what a GIS Specialist does is key to appreciating the value they bring to our data-rich future.