Global decision-making now depends on GIS (Geographic Information System) mapping as one of the most efficient strategies, which transforms raw geographic data into significant information.
GIS mapping is a crucial technology component needed by modern businesses to carry out their activities in the commercial development, agriculture, urban development, and emergency management sectors.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the GIS (Geographic Information System)
All forms of geographical data can be captured, stored, manipulated, analyzed, managed, and presented using a Geographic Information System (GIS). In order to visualize and analyze geographically referenced data, the GIS system is used to describe and characterize the earth and other geographies.
Sometimes, Geographic Information Science or Geospatial Information Studies are referred to by the acronym GIS. Any scientific endeavor that integrates data to assist researchers in visualizing, analyzing, and exploring spatially related material is referred to by the broad name “GIS.”
What is GIS Mapping?
System of Geographic Information (GIS) Mapping is the process of using GIS technology to create visual representations of data on maps. By converting intricate data sets into a comprehensible geographic format, it enables spatial interaction and analysis of information.
Additionally, by modeling future scenarios and trends using present data, GIS mapping enables predictive analysis, which is extremely useful for planning and decision-making. The capacity to instantly update maps with new data, guaranteeing that users always have access to the most recent information, is another important benefit.
Businesses use GIS mapping to identify high-potential market areas by analyzing demographic and geographic trends, environmentalists use it to track and map patterns of deforestation, and city planners use it to design and visualize urban expansion projects.
Benefits of GIS Mapping
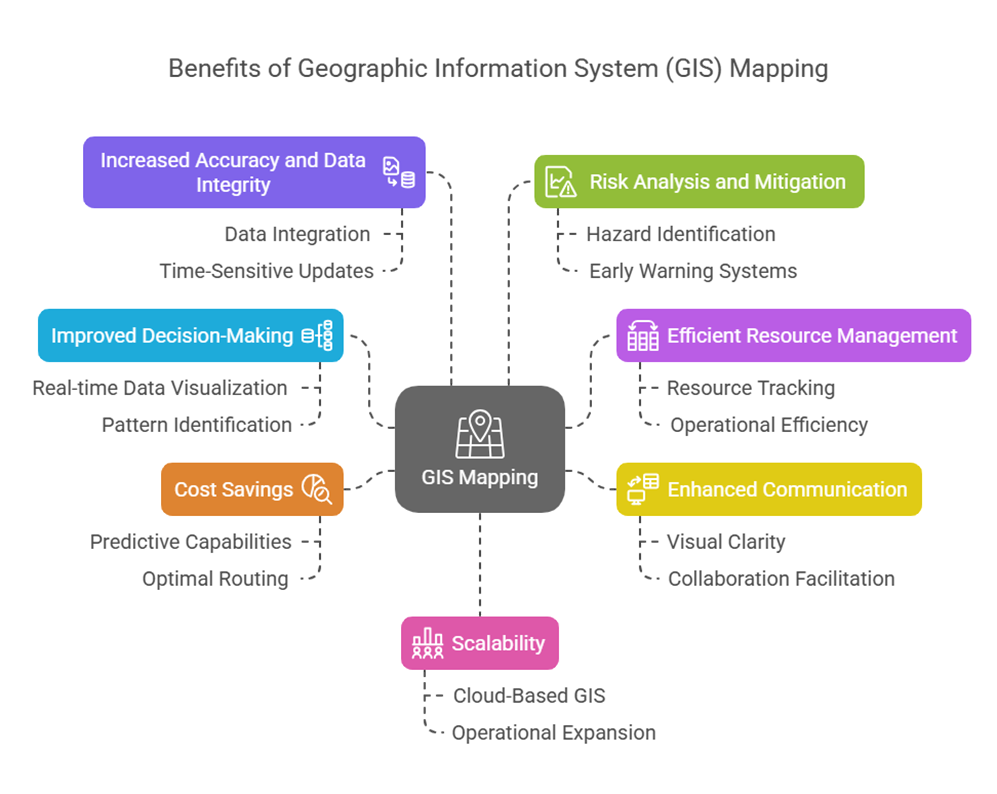
GIS (Geographic Information System) mapping technology provides valuable insights into data visualization, facilitating improved decision-making in a variety of fields. By effectively connecting spatial data with pertinent attributes, the system helps its users identify intricate patterns and linkages.
The system provides efficient resource planning by following land use developments and water resource patterns as well as biodiversity changes to help operators respond to emergency needs through live positioning capabilities and monitor environmental welfare. Following are some important benefits of GIS mapping:
Improved Decision-Making
The GIS makes it possible to see and analyze spatial data in real-time, enabling users to make data-supported decisions. While urban developers evaluate population demands after GIS research, public health professionals monitor the spread of disease. By enabling stakeholders to spot patterns and trends in the data along with related information, the geographical context gives them the ability to make strategic decisions.
Efficient Resource Management
Through the use of GIS technology, a company can monitor the patterns of resource distribution and consumption for water resources, energy reserves, and human workforce assets in certain regions. Managers can identify operational inefficiencies and reallocate firm resources to key places by using GIS. Organizations can minimize waste and maximize fertilizer use by using GIS to monitor agricultural irrigation zones and evaluate soil quality.
Enhanced Communication
GIS maps translate complex data into visually appealing formats that a wide range of users can understand. This visual clarity bridges the communication gaps between decision-makers like CEOs or politicians and technical teams like GIS analysts or engineers. When everyone knows the facts, it is easier to collaborate and reach an agreement.
Cost Savings
GIS enhances an organization’s capacity for planning and prediction, which leads to improved budget stewardship. GIS is used by building companies to assess the appropriateness of properties and avoid expensive delays caused by unforeseen topographical hazards.
In logistics operations, using GIS for optimized routing results in faster deliveries and lower fuel expenses. GIS is used by disaster management organizations to strategically allocate their resources, preventing expensive emergency responses.
Increased Accuracy and Data Integrity
Information gathered from field surveys, historical documents, and satellite imagery is used in the construction of GIS platforms. Cross-validation and error correction are made possible by the integration, guaranteeing the final maps’ remarkable accuracy. Since static cartographic maps quickly lose their value, time-sensitive updates via GIS mapping preserve the true value and relevance of the data.
Risk Analysis and Mitigation
GIS’s capacity to recognize dangerous man-made locations in addition to natural disaster zones is essential for the effective identification of sensitive areas that need hazard management. The technology assists users in assessing vulnerabilities in a variety of possible situations. By enabling them to create early warning systems, evacuation plans, and risk reduction strategies, this knowledge helps governments and organizations improve community resilience.
Scalability
A feature of geographical information systems is scalability that enables organizations to manage from one construction site up to national agricultural datasets. Organizations from any size group can now run their spatial data management across multiple geographical areas through cloud-based GIS without spending substantial infrastructure costs. The ability of GIS to expand makes it fit for use within local and regional and international operational areas.
GIS Mapping vs Traditional Mapping: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | Traditional Mapping | GIS Mapping |
| Data Handling | Static, manual updates | Dynamic, real-time updates |
| Interactivity | Limited | Highly interactive and analytical |
| Analysis | Visual inspection only | Advanced spatial analysis |
| Accuracy | Subject to human error | High, with automated data validation |
| Scalability | Labor-intensive expansion | Effortless scaling and integration |
Traditional Mapping
Static paper-based maps exist under the traditional mapping term that derives from human surveying and drafting tools and satellite imagery. These maps need total redraw or reprint because their original usage focuses on serving as reference documents yet assisting navigation and serving as presentation tools.
These maps depend only on visual viewing but do not provide interactive analysis features. Maps of traditional design often present inconsistent accuracy which both humans and out-of-date information limit. The feature integration of multiple analytical data layers through traditional maps remains impossible because they function as solitary entities.
GIS Mapping
Digital tools are used in GIS (Geographic Information System) mapping to gather, store, analyze, and interpret geographic data in a dynamic and interactive manner. With the use of data-rich platforms, GIS maps allow users to overlay, zoom in, filter, and do intricate geographic analysis, including spotting patterns, forecasting trends, and assessing environmental hazards.
While including vast datasets such as population, land use, hydrology, and climate data, GIS guarantees accuracy through the use of GPS and remote sensing technologies. These maps are easy to distribute on digital platforms, expandable, and updated frequently.
Benefits of GIS Mapping Over Traditional Maps
The advantages of GIS mapping over traditional mapping are as follows:
Real-Time Data Updates
One of the main benefits of GIS mapping over traditional maps is its ability to reflect real-time data updates. GIS platforms can instantly update to reflect changes in land use mapping, infrastructure, population, or topography, while traditional maps require manual updating and quickly become out of date. This ensures that decision-makers always have access to the most accurate and current information.
Multi-Dimensional Analysis
Traditional maps have limited analytical potential and are mostly used as visual aids. However, GIS facilitates multi-dimensional geographical analysis, allowing users to identify patterns, correlations, and trends. Static maps simply cannot compare to the amount of knowledge that GIS provides when analyzing the effects of urban expansion or identifying high-risk flood zones.
Predictive Modeling
Using historical and current data, GIS is a powerful tool for predictive modeling, which forecasts future events. Health officials can predict the spread of disease, urban planners can model city growth, and environmentalists can foresee patterns in deforestation. GIS’s capacity for forward-thinking gives it a major edge in proactive decision-making.
Customized Layers
One of the most noteworthy aspects of GIS is the ability to add customized data layers. Users can overlay demographic information, utility networks, zoning regulations, environmental risks, and even sales figures. This customization feature allows professionals from a range of industries to alter maps to suit their own operational or analytical needs.
Mobile Accessibility
Because modern GIS systems are mobile accessible, maps and data can be viewed, edited, or verified on smartphones and tablets. As on-site real-time data access leads to quicker and more accurate answers, this is especially helpful for fieldwork in emergency response, construction, surveying, and agriculture.
Automation and AI Integration
GIS platforms can now be connected with machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to automate data classification, trend detection, and predictive analytics. AI-powered models, for example, can forecast traffic jams or natural disasters, and satellite images can be automatically analyzed to detect changes in the land cover.
Better Visualization for Stakeholders
Last but not least, GIS excels in displaying complicated data. Raw data tables are more difficult for stakeholders, lawmakers, investors, and the general public to understand than maps and dashboards. Using GIS, technical data is converted into visually understandable visualizations that help with risk explaining, support collecting, and collaborative decision-making.
How GIS (Geographic Information System) Mapping Used?
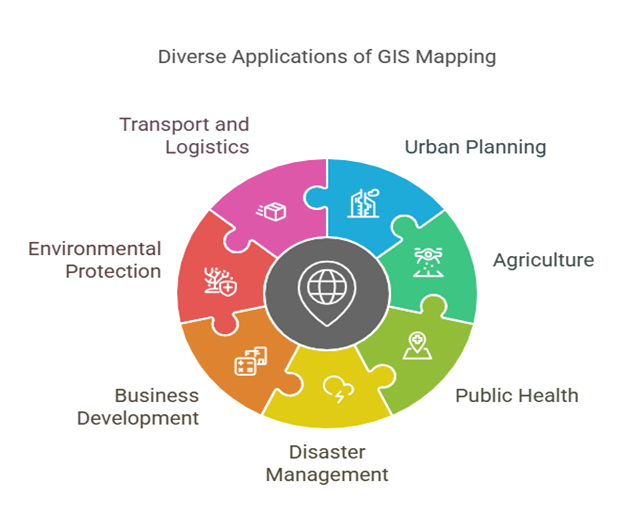
GIS (Geographic Information System) mapping is a powerful technology that lets users display, analyze, and understand geographical data in meaningful ways. Its applications span numerous industries and are revolutionizing our decision-making, planning, and response processes. Below is a more thorough explanation of how GIS mapping is used in each sector:
GIS Use in Urban Planning
GIS mapping transforms urban planning by enabling the development of more clever and efficient city plans. It guides the strategic planning of utilities including energy, sewage, and water supply networks, as well as the optimization of transportation systems and zoning regulations. Urban planners utilize GIS for site suitability assessments to identify the optimum places for commercial, industrial, or residential development. This leads to sustainable urban growth and improved resource management.
Agriculture and Irrigation
In agriculture, GIS mapping is essential to precision farming. It assists farmers with soil analysis, crop health monitoring with satellite imaging, and irrigation schedule management based on climatic and spatial data. Additionally, GIS makes yield forecasting easier by integrating environmental and historical data. These tools prevent resource waste, boost productivity, and reduce the environmental impact on farmlands.
Public Health
GIS is a crucial tool in public health for controlling and displaying disease outbreaks. It helps medical personnel assess the spread of infectious diseases, identify geographic clusters of illnesses, and allocate medical resources effectively. By mapping population density, sensitive areas, and access routes, GIS also helps with decisions about the sites of hospitals, immunization centers, and mobile health units. It is also used to evaluate environmental health concerns, such air pollution or contaminated water supplies.
Disaster Management
In disaster management, GIS is frequently used to enhance response and preparedness strategies. It helps forecast natural disasters like earthquakes, floods, and wildfires by modeling dangerous areas. During emergencies, GIS aids in the planning of evacuation routes, locating shelters, and tracking developments in real time. After a disaster, it is essential for policy responses, restoration, assistance coordination, and damage assessment.
Business Development
Businesses utilize GIS for spatial market research and strategic expansion. GIS enables customer demographic and purchasing behavior analysis, office or retail site selection, and market segmentation. By mapping the locations of their rivals and sales performance, businesses may maximize the impact of their marketing and resource allocation plans.
Environmental Protection
Initiatives for environmental monitoring and conservation commonly employ GIS which enables the tracking of deforestation, habitat loss, and changes in land use patterns. Conservationists utilize GIS to map biodiversity hotspots, monitor endangered species, and pinpoint air and water pollution sources. The data-driven insights provided by GIS facilitate the development of effective environmental protection policies and initiatives.
Transport and Logistics
In the transportation and logistics sector, GIS helps with fleet management, infrastructure design, and route optimization. Road condition analysis, fuel-efficient route planning, and real-time vehicle tracking are a few of its applications. GIS also helps with long-term planning by identifying major roadways and suggesting the best locations for ports, maintenance facilities, and logistical hubs.
AI Geo Navigator | Advanced GIS Mapping Solutions
Have a project in mind? Let’s map the way forward
Contact UsIn addition to making maps, AI Geo Navigator uses spatial data to provide intelligence.
Thus, the following are some of the services offered by Smart GIS Mapping:
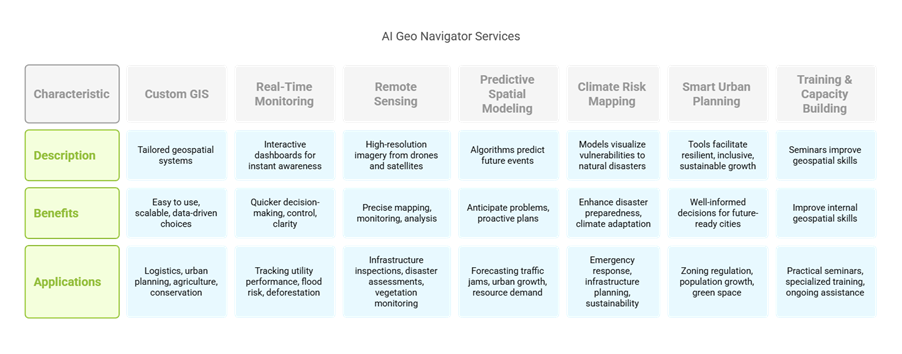
Custom GIS Solutions
At AI Geo Navigator provide unique GIS solutions that are especially suited to operating needs. Whether you operate in logistics, urban planning, agriculture, or environmental conservation, our team creates geospatial systems that work in unison with your processes. These tools are easy to use, scalable, and designed to help all levels of your company make data-driven choices.
Real-Time Monitoring Dashboards
Using real-time monitoring dashboards, clients can view real-time updates and track changes in particular areas of interest, such as assets, infrastructure, environmental conditions, or demographic trends. These interactive dashboards facilitate immediate awareness and quicker decision-making by combining multiple data layers into a single, visible platform. Our dashboards provide you with information and control over issues like utility performance, flood risk, and deforestation.
Remote Sensing Integration
They supplement GIS mapping with high-resolution imagery from satellites and drones by incorporating remote sensing. This imagery provides complete, up-to-date visual data that improves spatial layers and facilitates more accurate mapping, monitoring, and analysis. Applications range from monitoring vegetation and classifying land cover to disaster assessments and infrastructure inspections.
Predictive Spatial Modeling
Advanced algorithms and machine learning are used by predictive spatial modeling services to forecast future occurrences. The models let businesses foresee issues and take preventive measures, from predicting traffic congestion and urban growth to evaluating the demand for natural resources or environmental degradation. This innovative approach is very beneficial to clients managing long-term projects or high-risk operations.
Climate Risk Mapping
AI Geo Navigator is a climate risk mapping expert with its tools for modeling and visualizing vulnerabilities to natural catastrophes like as heat waves, landslides, floods, and droughts. These services are crucial for governments, non-governmental organizations, and businesses seeking to improve their plans for disaster preparedness and climate adaptation. As a result, they provide maps that support environmental sustainability initiatives, infrastructure development, and disaster response.
Smart Urban Planning Tools
Provide intelligent urban planning tools to cities and municipalities to facilitate resilient, inclusive, and sustainable growth. These tools aid in zoning regulation visualization, population growth analysis, green space distribution assessment, and infrastructure expansion simulation. In order to create future-ready urban landscapes, city planners can make well-informed decisions by incorporating various information into interactive GIS platforms.
Training and Capacity Building
In addition to technology, AI Geo Navigator makes training and capacity building investments to guarantee that your staff are completely prepared to administer and operate GIS systems on their own. Provide practical seminars, specialized training, and ongoing assistance to improve the internal geospatial skills of your company. The objective is to create enduring value by equipping your staff with the skills and information they require.