Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are powerful tools that help us understand patterns, relationships, and trends based on location. From mapping city infrastructure to managing natural resources, application of GIS plays an important role in solving real-world problems across industries.
In this article, we explore 10 of the most impactful applications of GIS across diverse domains. These are not just theoretical use cases, they are shaping real-world policies, streamlining public services, advancing scientific discovery, and unlocking new economic opportunities.
Whether you are new to GIS or a seasoned professional looking to expand your understanding, this comprehensive guide will show you how Geographic Information Systems are revolutionizing the way we perceive and solve complex problems.
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to GIS Applications
Today, GIS is widely used across industries such as urban planning, agriculture, transportation, environmental management, public health, and more. With the integration of artificial intelligence, like AI Geo Navigator are making GIS more accessible, predictive, and real-time than ever before.
Whether it’s optimizing delivery routes, predicting natural disasters, or planning new urban developments, GIS provides the insights needed to improve efficiency, accuracy, and strategy.
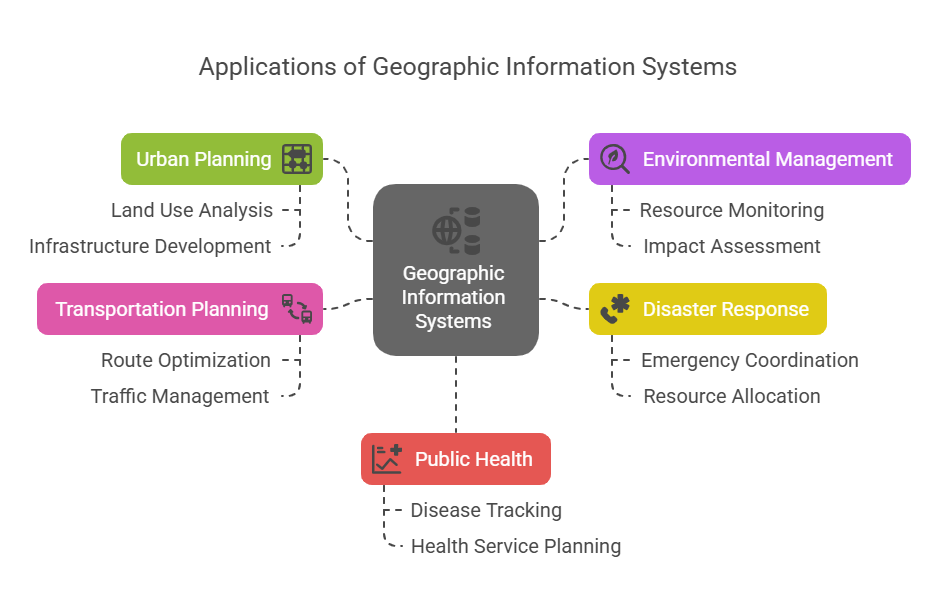
Applications of GIS in various industries
Urban Planning and Smart City Development
GIS has revolutionized urban planning by enabling professionals to make data-informed decisions about land use, transportation, zoning, and infrastructure development. Planners can overlay multiple spatial layers, such as demographic data, land value, and environmental constraints to evaluate the suitability of areas for housing, commercial zones, or public facilities.
This integration ensures that urban growth is managed in a sustainable and efficient manner. Real-time data from sensors and IoT devices can be mapped to visualize traffic patterns, monitor energy consumption, or detect anomalies in water supply systems.
Environmental Monitoring and Climate Change Adaptation
GIS plays a crucial role in understanding and mitigating environmental degradation. It allows researchers to track changes in land cover, forest density, water bodies, and biodiversity over time using satellite data.
These insights are essential for identifying hotspots of ecological stress and initiating timely interventions to prevent irreversible damage. GIS also supports pollution control by mapping industrial emissions, runoff sources, and air quality trends.
Climate change adaptation heavily relies on spatial data to assess risk and build resilience. By integrating historical climate data with predictive models, GIS can identify areas prone to floods, droughts, and heatwaves.
This enables policymakers to prioritize resource allocation, reinforce infrastructure, and plan relocation efforts. Additionally, it aids in designing early warning systems that can alert communities before extreme weather events strike.
Disaster Management and Emergency Response
Disaster management agencies use GIS to enhance preparedness and minimize the impact of natural and human-made disasters. Before a disaster strikes, GIS helps identify high-risk zones by analyzing terrain, historical incident data, and infrastructure vulnerability.
Planners use this data to develop evacuation routes, locate emergency shelters, and implement risk reduction strategies in the most exposed areas.
During and after disasters, GIS becomes a dynamic tool for real-time decision-making. Emergency response teams rely on updated maps to navigate blocked roads, assess damage, and locate stranded populations.
Relief logistics are optimized through spatial coordination of supply distribution points. After the crisis, GIS supports long-term recovery by mapping rebuilding efforts, tracking aid effectiveness, and planning for future resilience.
Agriculture and Precision Farming
In modern agriculture, GIS provides an essential framework for understanding field variability and enhancing productivity. Farmers and agronomists can collect and analyze spatial data related to soil type, moisture levels, elevation, and crop performance.
These insights allow for targeted application of fertilizers, irrigation, and pest control, reducing input waste and increasing yield efficiency.
Precision farming practices powered by GIS are transforming how agriculture is practiced, especially in regions facing climate and resource challenges. Temporal analysis of crop growth patterns enables early detection of disease or water stress, while weather-linked GIS tools help forecast optimal planting and harvesting windows.
Transportation and Infrastructure Planning
Transportation networks are the backbone of economic development, and GIS enables their design and management with maximum efficiency. It helps engineers and planners assess road conditions, traffic volumes, accident-prone zones, and connectivity gaps by analyzing spatial and temporal datasets.
Geography information system simulate traffic flow changes based on new developments, helping authorities make informed decisions about where to invest in road expansions, public transit systems, or pedestrian pathways.
In rural or underserved areas, GIS ensures inclusivity by highlighting communities lacking access to essential infrastructure.
Public Health and Disease Mapping
Public health planning increasingly relies on GIS to understand how location impacts health outcomes. By mapping disease outbreaks, hospital locations, vaccination coverage, and socio-economic factors, health officials can identify disparities and design targeted interventions.
This spatial awareness improves the precision of healthcare delivery and minimizes resource wastage in underserved areas.
During health crises like pandemics, GIS proves invaluable in real-time tracking of infection spread and healthcare system capacity. It helps in visualizing hotspots, predicting vulnerable zones, and monitoring intervention effectiveness.
Long-term, GIS contributes to strategic health planning by correlating environmental factors such as air quality or proximity to waste sites with chronic disease patterns.
Real Estate and Land Management
GIS provides a data-rich lens through which land development and real estate decisions can be evaluated. It helps assess factors such as land elevation, proximity to amenities, zoning regulations, and historical land use.
These insights improve site selection accuracy, investment forecasting, and risk assessment in both urban and rural property development.
From a governance perspective, GIS facilitates land management by maintaining up-to-date cadastral records and integrating legal boundaries with administrative data. This helps prevent disputes, improve tax collection, and support land reforms.
It also enables authorities to visualize land availability and optimize land use planning to align with economic and environmental goals.
Natural Resource Management
GIS is an indispensable tool for the strategic management of natural resources. By integrating geospatial datasets from remote sensing, field surveys, and historical records, stakeholders can monitor forests, water bodies, mineral reserves, and wetlands with greater precision.
GIS allows decision-makers to detect trends such as over-extraction, illegal encroachment, or ecosystem degradation, enabling them to enforce regulations and take corrective action proactively.
In policy and planning, GIS supports the development of sustainable use frameworks by identifying resource-rich areas and assessing their long-term viability. For instance, hydrological modeling in GIS can guide water resource allocation, while land suitability analysis informs reforestation or conservation initiatives.
These spatial insights help align resource exploitation with environmental thresholds, balancing development needs with ecological preservation.
Utilities and Asset Management
Utility providers face the complex task of maintaining extensive networks of physical assets, and GIS plays a central role in streamlining that process. It allows companies to map, monitor, and manage water pipelines, electricity grids, gas lines, and communication infrastructure in real time.
This spatial awareness ensures that operational teams can locate faults quickly, prioritize repairs, and reduce service downtime. Beyond maintenance, GIS contributes to forward-looking infrastructure planning by identifying trends in demand and service coverage gaps.
As urban populations grow, utility providers use GIS to plan system expansions and upgrades that anticipate future load and demographic shifts. Asset tracking, combined with condition-based data, also enables predictive maintenance, reducing costs and extending asset life cycles.
Tourism Development and Cultural Preservation
Tourism planners use GIS to design experiences that are geographically efficient, culturally rich, and environmentally sustainable. By mapping tourism assets, accessibility routes, seasonal trends, and visitor demographics, stakeholders can develop strategies that balance economic gains with minimal ecological and cultural disruption.
In cultural preservation, GIS helps catalog and monitor heritage sites, sacred landscapes, and architectural landmarks. By digitizing historical maps and overlaying them with current satellite data, authorities can detect changes and threats, such as urban encroachment, pollution, or erosion.
This spatial intelligence ensures timely interventions and policy measures that protect intangible and tangible heritage for future generations.
Let AI Geo Navigator Guide Your GIS Strategy
Whether you’re in urban planning, agriculture, logistics, or environmental management, our AI-powered GIS solutions help you visualize data, analyze patterns, and make smarter decisions.
From mapping and spatial analysis to predictive modeling and real-time insights, we bring the power of GIS to your business, quickly, accurately, and cost-effectively. Let us help you turn complex location data into actionable strategies that drive results.
Searching for Advanced GIS Solutions? Contact UsFinal Thoughts:
Application of GIS has become a strategic necessity in nearly every industry. As demonstrated throughout this guide, application of GIS empowers decision-makers to visualize trends, optimize operations, respond to emergencies, and plan for sustainable growth.
Whether managing urban infrastructure, improving agricultural efficiency, or preserving cultural heritage, GIS delivers the spatial insights needed to solve complex problems. With the integration of artificial intelligence, platforms like AI Geo Navigator are redefining how organizations leverage the application of GIS.
By combining AI with geospatial intelligence, businesses and governments can access predictive models, real-time analytics, and user-friendly tools that turn raw location data into powerful, actionable strategies.
FAQs on GIS Applications
What is GIS and how is it used in daily life?
GIS (Geographic Information Systems) is used to capture, store, and analyze spatial data. In daily life, it powers your GPS navigation, weather forecasts, and even delivery tracking apps.
Which industries use GIS the most?
Top industries include urban planning, agriculture, transportation, environmental science, disaster management, public health, and real estate.
What are the benefits of using GIS technology?
1. Improved decision-making
2. Real-time situational awareness
3. Better resource allocation
4. Increased operational efficiency
5. Enhanced visual communication
How is GIS different from GPS?
GPS gives you your current location, while GIS helps analyze and interpret spatial data across time and geography.
How does AI Geo improve GIS applications?
AI Geo enhances GIS by automating data analysis, detecting patterns faster, improving predictions, and enabling real-time decision-making through machine learning models.