A day in the life of a GIS specialist involves more than just mapping; it’s about solving real-world problems using spatial analysis, advanced software and a keen eye for detail. From field data collection to creating dynamic dashboards, Gis professionals bridge the gap between data and decision-making.
Table of Contents
ToggleGIS Specialists: Who Are They?
The job of a GIS Specialist calls for experts who transform spatial data into valuable organizational decisions through data interpretation and analysis.
The field of GIS positions specialists between geography and technology and data science where they operate specialized software to collect and display geospatial data. Each sector needs GIS Specialists to perform their vital tasks in urban planning along with environmental conservation and public health and disaster response.
The core part of their work consists of taking raw geographic data to generate understandable insights for making decisions. The professionals at their position generate geographic data collections highlighting flood-prone risks alongside traffic pattern assessment and wildlife movement tracking. The primary digital assets GIS Specialists use includes ArcGIS together with QGIS while utilizing remote sensing software.
The education background for most GIS Specialists comprises geography along with environmental science and urban planning and computer science. GIS Specialists integrate technical capabilities with sharp spatial capabilities which enable them to understand physical spatial relationships between data points.
Spatial data has become essential for decision making which results in expanding global demand for GIS specialists. When city planners seek advice or humanitarian teams need crisis response GIS Specialists make sure geographic facts support better decision outcomes.
What Do GIS Specialists Do?
The spatial information entered into GIS systems enables specialists to create vital visual elements that enhance organizational decision-making potential. Proficient command of daily remote sensing software requires Advanced ArcGIS alongside QGIS among other tools.
Their duties include data gathering and spatial data evaluation which results in data presentation tasks. GIS specialists integrate multiple data groups that combine geographical land features with demographic statistics alongside information about geographic use and infrastructure design procedures to establish interactive cartographic models.

At the beginning of their work GIS specialists’ source dependable data from both field research and satellite imagery while making use of openly available datasets. The gathered data needs proper cleaning and standardization methods before users can ensure its precise and uniform quality. The application of GIS tools enables spatial analysis by helping professionals to identify unexpected patterns in uncleaned datasets.
GIS Specialists utilize flood analysis data to predict disasters while they create satellite-based deforestation maps and choose retail sites through confirmed customer statistics. GIS Specialists generate visual displays through reports and dashboards as well as maps which provide information to users who manage technical data and complex statistics.
GIS Specialists need good communication skills combined with analytical abilities and detailed work ethics according to modern standards. As part of their duties GIS Specialists convert database processes into spatial visualizations for climate strategy planning and urban development through data science practices.
A Day in the Life of a GIS Specialist
A GIS Specialist combines daily work activities which integrate technical data evaluation with information visualization alongside strategic teamwork.
Reviewing Project Goals
The initial responsibility of each day involves performing a task review. Flood map updating, land use mapping analysis or survey planning serve as typical tasks during this phase. The project understanding enables workers to define their work attention throughout the day.
Processing and Cleaning Spatial Data
Most of the day during morning session focuses on importing data together with its preparation. The data preparation step removes formatting issues while converting different file types into layers which can be achieved through ArcGIS Pro or QGIS platforms. This step requires absolute precision to succeed.
Conducting Spatial Analysis
Specialists engage in analysis activities during the middle part of the day for mapping functions and distance calculations as well as spatial pattern recognition. The obtained data points become crucial references which enable better on-the-ground decisions.
Collaborating with Teams
The afternoons at the office involve meetings where specialists interact with planners as well as engineers and environmental consultants. Technical results should be presented so operating teams can understand them while generating practical solutions.
Map Data Visually with Dashboard Integration
The primary purpose of GIS goes beyond database management since it allows people to share insights through map presentations. Specified visual communications include interactive dashboards as well as storyboards and charts to present geographic patterns in a clear manner.
Quality Control and Planning
GIS professionals conduct metadata verification and map element confirmation as well as data storage verification before finishing their daily work. Prior to concluding work each day GIS professionals arrange their upcoming data needs and specific assignments.
The specialist concludes their work by documenting metadata while performing last quality assessments along with preparing activities for the following day. Professionals in this field require both detail-oriented skills and creative abilities through which they apply geographic data that has direct real-world effects.
What is the workplace of a GIS Specialist like

A GIS Specialist’s work environment requires both periods of attentive data analysis together with dynamic teamwork collaboration. Each of the professional environments where GIS Specialists work based on projects while handling data either within government-agencies or private firms or research institutions or non-profits.
The majority of work hours for GIS Specialists consists of computer work at dual displays with specialized software programs including ArcGIS, QGIS and ENVI. The system architecture is designed to maximize efficiency during data evaluations and map generation tasks and spatial model operations. Data analysts serve as the professional and organizational benchmark for the workspace and workers focus on technical systems.
Field work represents a part of regular duties for people who perform this type of job. Specialist professionals make site visits to gather GPS data while surveying satellite images and providing assistance to survey groups on location. Traveling to field locations introduces variety into the work while maintaining digital analysis through direct observation of the real world.
The culture is usually collaborative. Planners alongside environmental scientists and urban developers along with IT professionals are common counterparts for GIS Specialists in their daily work life. GIS Specialists find their workplace settings either in open-plan office spaces or both as part of GIS laboratories or alternative work arrangements which support flexible remote methods.
Working at this place maintains a high degree of attention to detail while having direct positive effects on operations. GIS Specialist environment provides dual support for technical precision and creative geospatial thinking through its operations for deforestation mapping and transportation route planning.
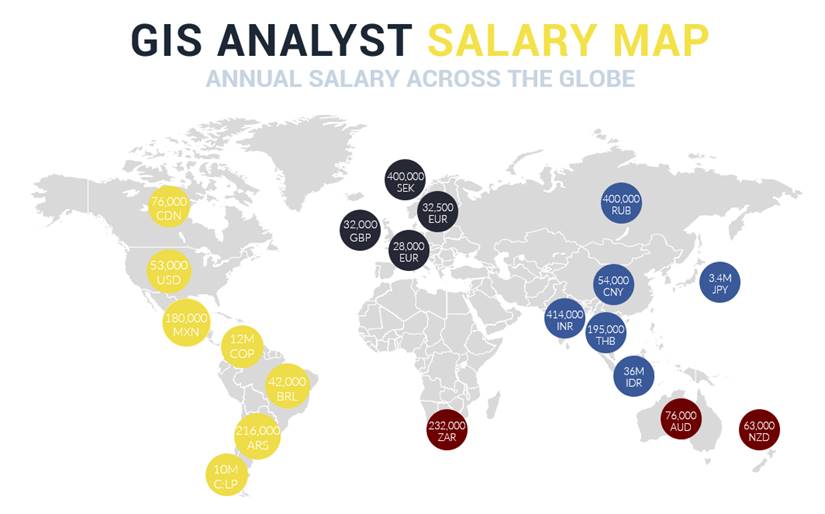
GIS Specialist Salary: How Much Do They Make?
The evaluation of spatial data through GIS Specialists produces vital information that guides organizational decisions in multiple sectors. The compensation for GIS Specialists depends on their workplace location along with their historical experience and industrial background.
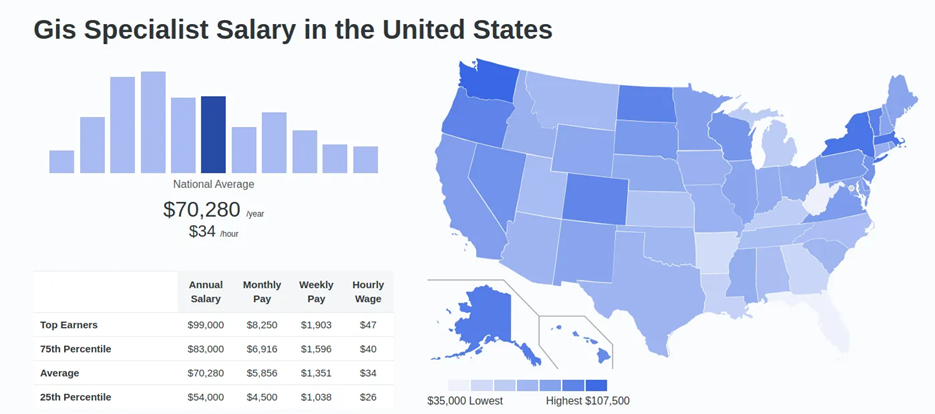
GIS Specialist salary in United States
A GIS Specialist typically receives $69,771 per year across the United States yet their starting salary reaches $47,929 while experienced workers can earn up to $101,568. These geographic areas of Raleigh within North Carolina and Houston within Texas have managed to secure higher salary rates because of their strong local demand.
GIS Specialist salary in Pakistan
The annual compensation for GIS Specialists in Pakistan falls between PKR 2 Lac and PKR 3 Lac. The compensation of GIS Specialists rests on their professional background and workplace location since junior-level staff brings in lower wages but upper-level workers obtain better pay.
GIS Specialist salary in United Kingdom
University of La Verne Online reports median annual compensation for UK GIS Specialists meets £40,286. At entry level new professionals receive somewhere between £22,000 but more experienced professionals earn between £51,000. Users in Milton Keynes together with Reading benefit from better income since these areas face greater employment requirements.